Nutrition can be confusing — one minute fat is the enemy, whereas the next minute, we’re being told that we need more key ‘healthy’ fats. To demystify the confusion, we’re going to address the importance of the essential fatty acid, omega-3.
Since the human body cannot create this nutrient, it must be consumed through dietary sources. Why should you consume more omega-3 — and more importantly, what should you eat to increase your intake?
3 Surprising Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
From your heart to your brain, omega-3 fatty acids are critical for a wide range of bodily functions. Based on the available research, here are some of the top benefits — which will motivate you to increase your intake, starting today!
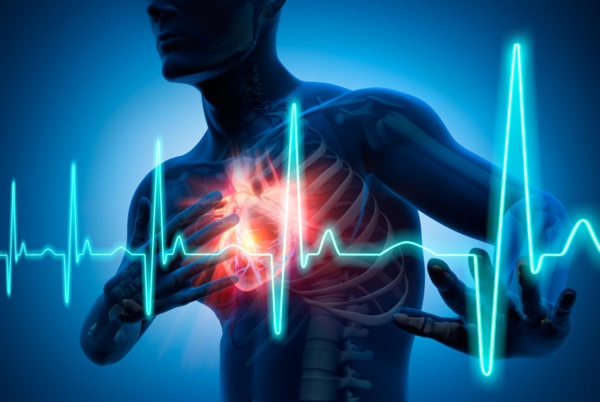
- Reduced risk of heart disease
When it comes to cardiovascular disease, the benefits associated with omega-3 are overwhelming. Just some of the benefits include a lower risk of abnormal heartbeats, fewer harmful fats in the blood, a reduction in artery plaque, and slightly lower blood pressure. Within one study, omega-3s were linked to a 6 percent lower risk of heart disease. The American Heart Association recommended consuming at least two servings of fish weekly.
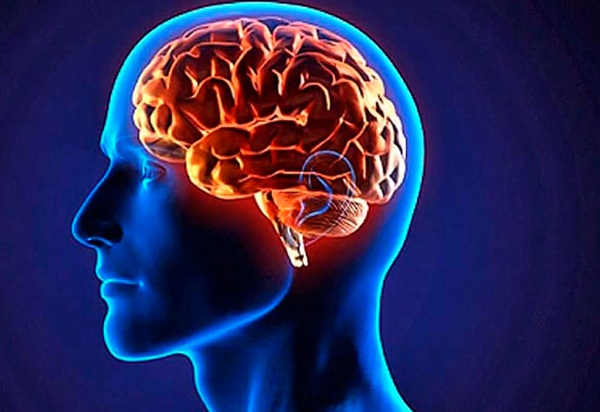
- Improved mental health
From depression to cognitive function, omega-3s have been vastly studied due to their positive effects on neural health. It has been found that these essential fatty acids offer anti-inflammatory benefits within the brain, reducing your risk of neurodegenerative conditions. Within one study, omega-3 was also shown to improve symptoms of major depressive disorder.
- Reduced inflammation
Inflammation can affect all areas of the body and is often contributed to diet. As stated by the University of Maryland Medical Center, omega-3s can reduce inflammation, furthering reducing your risk of cancer, arthritis, and heart disease. The research shows that diets high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in omega-6 fatty acids can help improve symptoms of osteoarthritis.
The Best Natural Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
It is recommended that you consume between 250 and 500 mg of DHA and EPA combined daily. While DHA and EPA are mainly found in oily fish and krill — there is also the plant-based form, known as ALA. When you consume ALA, your body will convert it into DHA and EPA in order to synthesize it.
Although fish is one of the most commonly discussed sources of omega-3, there are plenty of options — including delicious plant-based foods. If you would like to increase your intake, here’s where to begin:
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
- Pumpkin seeds and pumpkin seed oil
- Algal oil and krill
- Salmon, tuna, halibut, mackerel, trout, sardines, and herring
It’s time to reconsider your current daily diet, incorporating more healthy, omega-3 fatty acids while reducing your intake of low-quality, unhealthy fat sources.
After all, Ann Wigmore said it best, “The food you eat can either be the safest and most powerful form of medicine — or the slowest form of poison.” You decide.